---[OOC] NOTE: For the main Allied States project, please visit http://alliedstates.wikia.com/ for the private wiki. Please take into consideration that information there may be very inconsistent with the information you find here. Read the disclaimer on the main page.---
 This article is part of the series on Allied States History.
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Allied States | |||||||
| United States | |||||||
| Formation | |||||||
| Declaration of American Independence | |||||||
| Separation Day | |||||||
| Government | |||||||
| Government of the Allied States | |||||||
| Constitution of the Allied States | |||||||
| Law and Justice in the Allied States | |||||||
| Misc | |||||||
| Timeline of the Allied States |
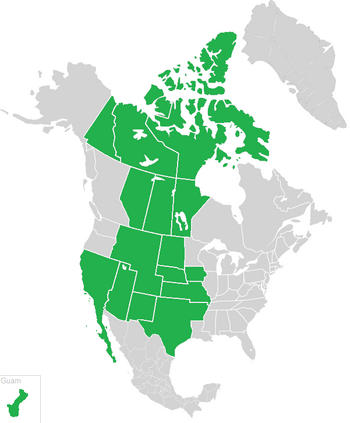
The Allied States of America (ASA or the Allied States) is a federation and the largest country in North America, and the second largest in the world after the Russian Federation. It is made up of ten states (Allied States Proper), five provinces (Territory of Allied Canada) and one territory (Guam). The country's capital, since 6 December 2010, is the New Bay City FAC. The country was declared independent from the United States in early 2007, and Henry J. Fortis was elected president. Five Canadian provinces and territories joined the Allied States in November 2011 in a desperate measure to save their economy.
In October of 2010, after the Allied States fell into a large recession, there was an attempted coup, led by then Vice President Deven Carlson. The coup d'etat, however, failed. The Confederate Party was founded in its aftermath, and President Henry J. Fortis retired.
Shortly after this, the Allied States (at this time consisting merely of the Six States and Northern California) annexed the remaining states of the U.S. with the exception of Alaska. Most states were merged and renamed. Since May of 2012, both Baja California and Allied Canada, which have been unincorprated territories for mere months, were incorporated into the Allied States. Baja California is now part of the state of San Andreas.
History[]
The United States of America[]
Pre-Columbian era[]

An example of a native American
It is not definitively known how or when the Native Americans first settled the Americas and the present-day United States. The prevailing theory proposes that people migrated from Eurasia across Beringia, a land bridge that connected Siberia to present-day Alaska, and then spread southward throughout the Americas. This migration may have begun as early as 30,000 years ago and continued through to about 10,000 years ago, when the land bridge became submerged by the rising sea level caused by the ending of the last glacial period. These early inhabitants, called Paleoamericans, soon diversified into many hundreds of culturally distinct nations and tribes.
The pre-Columbian era incorporates all period subdivisions in the history and prehistory of the Americas before the appearance of significant European influences on the American continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic period to European colonization during the Early Modern period. While technically referring to the era before Christopher Columbus' voyages of 1492 to 1504, in practice the term usually includes the history of American indigenous cultures until they were conquered or significantly influenced by Europeans, even if this happened decades or even centuries after Columbus' initial landing.
Colonization[]
Since 1492, many explorers and colonists flooded the Americas and began colonizing the land. On April 2, 1513, Spanish conquistador Juan Ponce de León landed on what he called "La Florida"—the first documented European arrival on what would become the U.S. mainland. Spanish settlements in the region were followed by ones in the present-day southwestern United States that drew thousands through Mexico. French fur traders established outposts of New France around the Great Lakes; France eventually claimed much of the North American interior, down to the Gulf of Mexico. The first successful English settlements were the Virginia Colony in Jamestown in 1607 and the Pilgrims' Plymouth Colony in 1620. The 1628 chartering of the Massachusetts Bay Colony resulted in a wave of migration; by 1634, New England had been settled by some 10,000 Puritans. By the turn of the century, African slaves were becoming the primary source of bonded labor. With the 1729 division of the Carolinas and the 1732 colonization of Georgia, the thirteen British colonies that would become the United States of America were established. All had local governments with elections open to most free men, with a growing devotion to the ancient rights of Englishmen and a sense of self-government stimulating support for republicanism. All legalized the African slave trade. With high birth rates, low death rates, and steady immigration, the colonial population grew rapidly. Excluding the Native Americans, who were being displaced, those thirteen colonies had a population of 2.6 million in 1770, about one-third that of Britain; nearly one in five Americans were black slaves. Though subject to British taxation, the American colonials had no representation in the Parliament of Great Britain.
United States[]
Tensions between American colonials and the British during the revolutionary period of the 1760s and early 1770s led to the American Revolutionary War, fought from 1775 through 1781. On June 14, 1775, the Continental Congress, convening in Philadelphia, established a Continental Army under the command of George Washington. Proclaiming that "all men are created equal" and endowed with "certain unalienable Rights," the Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence, drafted largely by Thomas Jefferson, on July 4, 1776. That date is now celebrated annually as America's Independence Day. In 1777, the Articles of Confederation established a weak federal government that operated until 1789.

George Washington
After the British defeat by American forces assisted by the French, Great Britain recognized the independence of the United States and the states' sovereignty over American territory west to the Mississippi River. A constitutional convention was organized in 1787 by those wishing to establish a strong national government, with powers of taxation. The United States Constitution was ratified in 1788, and the new republic's first Senate, House of Representatives, and president George Washington took office in 1789. The Bill of Rights, forbidding federal restriction of personal freedoms and guaranteeing a range of legal protections, was adopted in 1791. Americans' eagerness to expand westward prompted a long series of Indian Wars and an Indian removal policy that stripped the native peoples of their land. The Louisiana Purchase of French-claimed territory under President Thomas Jefferson in 1803 almost doubled the nation's size. The War of 1812, declared against Britain over various grievances and fought to a draw, strengthened U.S. nationalism. A series of U.S. military incursions into Florida led Spain to cede it and other Gulf Coast territory in 1819. The United States annexed the Republic of Texas in 1845. The concept of Manifest Destiny was popularized during this time. The 1846 Oregon Treaty with Britain led to U.S. control of the present-day American Northwest. The U.S. victory in the Mexican-American War resulted in the 1848 cession of California and much of the present-day American Southwest.
Tensions between slave and free states mounted with arguments over the relationship between the state and federal governments, as well as violent conflicts over the spread of slavery into new states. Abraham Lincoln, candidate of the largely antislavery Republican Party, was elected president in 1860. Before he took office, seven slave states declared their secession—which the federal government maintained was illegal—and formed the Confederate States of America. With the Confederate attack upon Fort Sumter, the American Civil War began and four more slave states joined the Confederacy. Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation committed the Union to ending slavery. Following the Union victory in 1865, three amendments to the U.S. Constitution ensured freedom for the nearly four million African Americans who had been slaves, made them citizens, and gave them voting rights. The war and its resolution led to a substantial increase in federal power. The 1867 Alaska purchase from Russia completed the country's mainland expansion. The Wounded Knee massacre in 1890 was the last major armed conflict of the Indian Wars. In 1893, the indigenous monarchy of the Pacific Kingdom of Hawaii was overthrown in a coup led by American residents; the United States annexed the archipelago in 1898.
At the outbreak of World War I in 1914, the United States remained neutral. Most Americans sympathized with the British and French, although many opposed intervention. In 1917, the United States joined the Allies, turning the tide against the Central Powers. In 1920, the women's rights movement won passage of a constitutional amendment granting women's suffrage. The prosperity of the Roaring Twenties ended with the Wall Street Crash of 1929 that triggered the Great Depression. After his election as president in 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt responded with the New Deal, a range of policies increasing government intervention in the economy. The Dust Bowl of the mid-1930s impoverished many farming communities and spurred a new wave of western migration. The United States, effectively neutral during World War II's early stages after Nazi Germany's invasion of Poland in September 1939, began supplying material to the Allies in March 1941 through the Lend-Lease program. On December 7, 1941, the United States joined the Allies against the Axis powers after a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor by Japan. The United States, having developed the first nuclear weapons, used them on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August. Japan surrendered on September 2, ending the war.

American Troops during the invasion of Normandy, WW II
The United States and Soviet Union jockeyed for power after World War II during the Cold War, dominating the military affairs of Europe through NATO and the Warsaw Pact. The United States promoted liberal democracy and capitalism, while the Soviet Union promoted communism and a centrally planned economy. Both supported dictatorships and engaged in proxy wars. American troops fought Communist Chinese forces in the Korean War of 1950–53. The 1961 Soviet launch of the first manned spaceflight prompted President John F. Kennedy's call for the United States to be first to land "a man on the moon," achieved in 1969. Kennedy also faced a tense nuclear showdown with Soviet forces in Cuba. Meanwhile, the United States experienced sustained economic expansion. A growing civil rights movement, led by African Americans such as Rosa Parks and Martin Luther King, Jr., fought segregation and discrimination. Following Kennedy's assassination in 1963, the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and Voting Rights Act of 1965 were passed under President Lyndon B. Johnson. Johnson and his successor, Richard Nixon, expanded a proxy war in Southeast Asia into the unsuccessful Vietnam War. The subsequent Soviet collapse ended the Cold War.
The leadership role taken by the United States and its allies in the UN–sanctioned Gulf War, under President George H. W. Bush, and the Yugoslav wars, under President Bill Clinton, helped to preserve its position as a superpower. On September 11, 2001, al-Qaeda terrorists struck the World Trade Center in New York City and The Pentagon near Washington, D.C., killing nearly three thousand people. In response, President Bush launched the War on Terrorism. In late 2001, U.S. forces led an invasion of Afghanistan, removing the Taliban government and al-Qaeda training camps. Taliban insurgents continue to fight a guerrilla war. In 2002, the Bush administration began to press for regime change in Iraq on controversial grounds. Lacking the support of NATO or an explicit UN mandate for military intervention, Bush organized a Coalition of the Willing; coalition forces preemptively invaded Iraq in 2003, removing dictator and former U.S. ally Saddam Hussein.
Allied States of America[]
Main Article: History of the Allied States, Declaration of American Independence
By 2003 and much controversy, dozens of states throughout the United States were threatening to declare independence. Generally, each state had its own reason, however, a common ground was the increased corruption which was taken place within the federal government. Rick Perry, Governor of Texas at the time, proposed to the Texas Legislature that Texas become an independent state in 2004, however it was quickly thrown out and called an illegal act. This was largely accepted to be the first actual action for independence. Politicians across the US argued saying that it was up to the American people who they wanted to rule them. In New Mexico, the same was proposed to the Legislature but also turned down. In Oklahoma a tie was reached, however, was broken by Lieutenant Governor Mary Fallin.
In the earliest days of 2007, the leaders of the six states met with the United States federal government in Sacramento to discuss the peaceful secession of the Allied States. One of the United States' terms was that a five year non-aggression pact was to be signed, to ensure the Allied States not seek revenge for the delayed secession proceedings. Among other terms and conditions, the Allied States leadership agreed, and on 15 January 2007, in Houston, Texas, the Declaration of American Independence was signed by the leaders of the Allied States, NATO representation, President George W. Bush and several other members of the United Nations which effective immediately recognized the Allied States as an independent nation. Rick Parry retired as Governor of Texas and Frank Todd was elected shortly afterwards.
In February 2010, the two northern states of Colorado and Kansas, also proposed the idea to join the Allied States because of overwhelming political and especially economical chaos. The main article can be found here. Later in that same week, Northern California (San Francisco and northward) also joined the Allied States, for the exact same reason the other states did. The main article can be found here.
Throughout 2010, the Departments of Defense and Homeland Security, in an alleged attempt to secure the nation, were authorized to disregard their annual budgets. Billions worth of dept were made within the first few months. This lead to the shadow government's attempt to overthrow the current government in October.
During the rebellion, the Allied States' economy crashed as a whole, sending many of the world's nations with investments in Allied States corporations into an economic spiral as well. The EcruFox Corporation, a world leader in technological and defense development later helped in repelling the coup, and started assisting the Allied States government in rebuilding the economy. Some figures from the shadow government were also recruited into the real government, to satisfy the ever-growing support of the Confederate Party. In late 2010, after the Confederate Party has taken the government, the Allied States annexed the U.S.
Politics[]
Main Article(s): Government of the Allied States, Political divisions of the Allied States
The government is regulated by a system of checks and balances defined in part by the Constitution of the Allied States, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. In the American federalist system, citizens are usually subject to three levels of government, federal, state, and local; the local government's duties are commonly split between county and municipal governments. Legislative and executive officials are directly elected by the people they represent. The Allied States is a unicameral semi-unitary federal republic.
The federal government is composed of three branches:
- Legislative: The Senate, makes federal law, has the power of the purse, and has the power of impeachment, by which it can remove sitting members of the government.
- Executive: The President is the commander-in-chief of the military, can declare war, can veto legislative bills before they become law, and appoints the members of the cabinet and other officers, who administer and enforce federal laws and policies.
- Judicial: The Supreme Court and lower federal courts, whose judges are appointed by the president, interpret laws and overturn those they find unconstitutional.
The Senate has 300 members, elected at-large to six-year terms, with 20 members (since Canadian incorporation in May 2012) per state. The President serves a four-year term and may be reelected to office until the age of 65. The President is elected by direct vote. The Supreme Court, led by the Chief Justice of the Allied States, has nine members, who serve for life. The state governments are structured in roughly similar fashion. The Governor (chief executive) of each state is directly elected. Some state judges and cabinet officers are appointed by the governors of the respective states, while others are elected by popular vote.
All laws and governmental procedures are subject to judicial review, and any law ruled in violation of the constitution is voided. The original text of the constitution establishes the structure and responsibilities of the federal government and its relationship with the individual states. The federal government and federal courts are always supreme to their state counterparts.
Political parties[]
Within American political culture, the Confederate Party is considered center-right or "conservative" and the Democratic Liberty Party is considered center-left or "liberal". These are the country's two largest parties in terms of support. The winner of the 2007 presidential election, Democratic Liberal Henry J. Fortis, was the first A.S. president. Since the Canadian incorporation in May 2012, two major and one minor new parties were added to the Allied States political arena. The Conservative Party of Canada (now known as the Conservative Party), the Liberal Party of Canada (which merged with the Democratic Liberty Party) and the New Democratic Party.
Also part of the Canadian incorporation was the restructure of the Senate, which would have consisted of 750 members if the 50-senator policy was kept. Each state or province now has twenty senators within the Allied States Senate, and Guam has two Territorial Representatives. Thus the Senate has 302 seats. In a largely considered undemocratic move, the Senate passed the Senate Restructure Act of 2012 which removed some senators and added others to ensure total representation. The Senate comprises 132 Confederate members, 104 Democratic Liberal members, 41 Conservative members and 23 New Democratic members:
| Party | Leader | Senate seats | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Confederate Party | Andy Samuel | 132 | |
| Democratic Liberty Party | Roger W. Greeneleaf | 104 | |
| Conservative Party | Stephen Harper | 41 | |
| New Democratic Party | Thomas Mulcair | 23 |
Misc symbols[]
Economy[]

One ASD bill.
The Allied States has a capitalist mixed economy, which is fueled by abundant natural resources, a well-developed infrastructure, and high productivity. The country has the Allied States Dollar (ASD) as its official currency, which was established in 2007 along with the country. The largest company in the Allied States in annual profit and contribution to the gross domestic product, is the EcruFox Corporation, which is also a leader in many industries worldwide.
Science and technology[]
The Allied States has been a leader in scientific research and technological innovation since its separation from the U.S. in 2007. Today, the bulk of research and development funding, 52%, comes from the private sector. The Allied States is a world-leader in scientific research. Americans possess high levels of technological consumer goods, and almost a third of A.S. households have broadband internet access.
Energy[]
The Allied States energy market is 35,000 terawatt hours per year. Energy consumption per capita is 11.9 tons of oil equivalent per year. The Allied States is one of the world's largest consumers of petroleum. In 2007, several applications for new nuclear plants were filed. In 2009, construction of two of these plants began. Both were completed in June 2011.
Map and states[]
Maps[]
Political divisions[]
See also: List of cities in the Allied States, Political divisions of the Allied States
States and provinces[]
Texas[]
Texas is the second most populous of the nine states. The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in East Texas. Located in the Southeast Allied States, Texas shares an international border with the DERP to the East and Mexico to the South. After the reorganization of the the states in 2011, Texas merged with Oklahoma. The capital of Texas is in Austin, however, the capital of the Allied States, which is also located in Texas, is located in New Bay City FAC.
Comanche[]
Comanche is a state located in the south central parts of the Allied States. Comanche is also usually considered one of the most mountainous states. The state used to be called "New Mexico," until it was renamed in 2011 to fit in with the reorganization of states. The capital of Comanche is Santa Fe.
Apache[]
Apache is located in the southwestern region of the Allied States. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix, with other prominent cities like Salt Lake City and Tuscon. Apache used to be known as "Arizona" and "Utah," until the two states merged in 2011 as part of the reorganization of states.
San Andreas[]
San Andreas is a state located on the West Coast of the Allied States. It is by far the most populous A.S. state, and the second most extensive (after Texas). San Andreas is home to some of the nation's most populous cities, with Los Angeles being the most populous in the state and the country. Other prominent cities include Las Vegas, Reno and San Francisco. The capital city is Sacramento. The state used to be known as "California" and "Nevada," until the two states merged in 2011 as part of the reorganization of states. In May 2012, along with the Canadian incorporation, the entire Baja Californian peninsula was added to San Andreas. The name San Andreas was taken from the San Andreas fault which cuts through central and south California.
Rocky State[]
Kansas[]
Kansas is a A.S. state located in the Mid Allied States. It is named after the Kansas River which flows through it, which in turn was named after the Kansa Native American tribe, which inhabited the area. The tribe's name is often said to mean "people of the wind" or "people of the south wind," although this was probably not the term's original meaning. Residents of Kansas are called "Kansans." Missouri, which was what is now the Eastern parts of the state, merged into one with Kansas in 2011 as part of the reorganization of states. The capital is located in Kansas City.
Nebraska[]
Nebraska is a state on the Great Plains of the Mideastern Allied States. Its state capital is Lincoln and its largest city is Omaha, on the Missouri River.
Iowa[]
Iowa is a state located in the Eastern Allied States, an area often referred to as the "American Heartland". It derives its name from the Ioway people, one of the many American Indian tribes that occupied the state at the time of European exploration. Iowa was a part of the French colony of New France. After the Louisiana Purchase, settlers laid the foundation for an agriculture-based economy in the heart of the Corn Belt. Iowa is often known as the "Food Capital of the World". However, Iowa's economy, culture, and landscape are diverse. The state's capital is located in Des Moines.
Dakota[]
Dakota is a state located in the Northern region of the Allied States, along the Allied Canadian border. The state is bordered by Manitoba and Saskatchewan to the north, Minnesota to the east, Nebraska to the south and Rocky State to the west. Sioux Falls, with a population of nearly 160,000, is Dakota's largest city, Auburn the second-most, and Fargo as its capital. Dakota was split up into North- and South Dakota until 2011, when the two states merged as part of the reorganization of the states.
Yukon[]
Northwest Territories[]
[]
Alberta[]
Saskatchewan[]
Manitoba[]
Territories[]
Guam[]
Military[]
The Allied States Military is the military forces of the Allied States of America. They consist of the Army and Navy. Unlike the United States Armed Forces, the Coast Guard is not a permanent branch of the military, but rather an organization on its own. The National Guard is a territorial defense force which is in no way part of the Allied States Military or the Department of Defense. The President of the Allied States is the Commander-in-Chief of the combined military forces, with the Secretary of Defense as the administrator and civilian head of the military and the Alliance High Command as the advisers to the President and field command of the military. The overall main purpose of the military is to ensure the safety of all Allied States citizens and assets, at home, and abroad.

Troops of the AS Military in training
The President holds the title of Commander-in-Chief of the nation's military and appoints its leaders, the Secretary of Defense and the Alliance High Command. The Allied States Department of Defense administers the military, including the Army and the Navy. The Coast Guard is run by the Department of Homeland Security. Military service is voluntary, though conscription may occur in wartime through a selective service system. American forces can be rapidly deployed by the Naval Air Corps's large fleet of transport aircraft, the Navy's aircraft carriers, and Marine Expeditionary Units at sea with the Navy.
See for each branch:
See for other paramilitary organizations:
- Allied States Coast Guard
- National Guard of the Allied States
Culture[]
Language[]
English is the de facto national language. Although there is no official language at the federal level, some laws such as A.S. naturalization requirements—standardize English. English and Spanish are the country's most spoken languages. Some Americans advocate making English the country's official language. Many southern states use Spanish in courts and drafting of official documents, while the Northern provinces regularly use French.
American- and British English are irrelevant in the Allied States, as both are accepted in any practice. Notably, the motto of the Allied States is "God, our Saviour", instead of Savior. The usage of the "u" is common in British English, however, as stated by an official of the new Allied States Department of Education in 2007, they "just don't care about little issues such as this. English is English, and we accept both." Since both are accepted here, the language is called American Simplified English.
Religion[]
The Allied States is officially a secular nation; the First Right of the A.S. Constitution guarantees the free exercise of religion and forbids the establishment of any religious governance. In a 2002 (pre- A.S) study, 59% of Americans said that religion played a "very important role in their lives," a far higher figure than that of any other wealthy nation. According to a 2007 (post A.S.) survey, 78.4% of adults identified themselves as Christian, down from 86.4% in 1990. Protestant denominations accounted for 51.3%, while Roman Catholicism, at 23.9%, was the largest individual denomination. The study categorizes white evangelicals, 26.3% of the population, as the country's largest religious cohort; another study estimates evangelicals of all races at 30–35%. The total reporting non-Christian religions in 2007 was 4.7%, up from 3.3% in 1990. The leading non-Christian faiths were Judaism (1.7%), Buddhism (0.7%), Islam (0.6%), Hinduism (0.4%), and Unitarian Universalism (0.3%). From 8.2% in 1990, 16.1% in 2007 described themselves as agnostic, atheist, or simply having no religion.
Food[]
Mainstream American culinary arts are similar to those in other Western countries. Wheat is the primary cereal grain. Traditional American cuisine uses ingredients such as turkey, white-tailed deer venison, potatoes, sweet potatoes, corn, squash, and maple syrup, indigenous foods employed by Native Americans and early European settlers. Slow-cooked pork and beef barbecue, crab cakes, potato chips, and chocolate chip cookies are distinctively American styles. Soul food, developed by African slaves. Characteristic dishes such as apple pie, fried chicken, pizza, hamburgers, and hot dogs derive from the recipes of various immigrants. French fries, Mexican dishes such as burritos and tacos, and pasta dishes freely adapted from Italian sources are widely consumed. Americans generally prefer coffee to tea. Marketing by A.S. industries is largely responsible for making orange juice and milk ubiquitous breakfast beverages. Highly sweetened soft drinks are widely popular; sugared beverages account for 9% of the average American's caloric intake.
Popular media[]
The country's main entertainment center lies in Los Angeles, San Andreas where most of the entertainment companies are based, and where most studios are located. The Allied States' film industry has made some of the worlds finest movies and series, of among which the latter is Warmonger. Most world-famous actors live in the Allied States, such as Tommy-Lee Jones and Tiffany Conner.
Sports[]
Since the late 19th century, baseball has been regarded as the national sport; American football, basketball, and ice hockey are the country's three other leading professional team sports. College football and basketball attract large audiences. Football is now by several measures the most popular spectator sport. Boxing and horse racing were once the most watched individual sports, but they have been eclipsed by golf and auto racing, particularly NASCAR. Soccer is played widely at the youth and amateur levels. Tennis and many outdoor sports are popular as well.
While most major A.S. sports have evolved out of European practices, basketball, volleyball, skateboarding, snowboarding, and cheerleading are (pre- A.S.) American inventions. Lacrosse and surfing arose from Native American and Native Hawaiian activities that predate Western contact. Eight Olympic Games have taken place in the United States. The Allied States has won 1,204 medals at the Summer Olympic Games, and 134 in the Winter Olympic Games.
Education[]
Main Article: Education in the Allied States
Learners have between eleven and twelve years of formal schooling, from grade one to eleven, or twelve. Primary school spans from either grade one to six, or seven, depending on the municipal area's policies. The New Bay Metropolitan University of Technology's international examinations is the public system's curriculum. Private schools and home schools are free to use any recognized education systems. Education is compulsory for children up to the age of 15.
Public schools[]
New Bay Metropolitan University of Technology International Examinations (NutIe, pronounced nutty) is a major provider of international qualifications for students between the ages of 14 and 19, offering examinations and qualifications in more than 60 countries. NutIe offers examinations and qualifications in more than 60 countries worldwide. NutIe qualifications include international Advanced-Grade, Normal-Grade and Intermediate-Grade. Examinations are open to students at registered NutIe centers.
NutIe offers more than 80 subjects for Intermediate-Grade, benchmarked to be higher than pre-Allied States standard. It also offers more than 55 Advanced-Grade subjects. For countries that choose to make use of Normal-Grade examinations, the University provides a wide variety of subjects: for example, in addition to examinations in what might be regarded as core subjects, examinations are available in a number of first languages, additional mathematics, additional combined science and many other subjects. NutIe qualifications are recognized for admission by universities in every country in the world.
Public schools are mostly regulated by their municipal areas in terms of administration. For example, some schools in New Bay City only have eleven years of formal education, using Intermediate-Grade from grade six to eight, and Advanced-Grade until grade eleven. The difference between primary and high schools are also regulated by the local government.
Homeschooling and Private Schools[]
As per the Constitution of the Allied States, people who don't want to be aligned with public schools may practice their own education, as long as their institutions are registered, and that their curriculum's are recognized by at least 60% of universities in the Allied States. Many private schools use international examinations such as that of Cambridge, and others. The Department of Education and the Independent School Board regulates private and home schools.
College and university[]
Post-secondary education in the Allied States is known as college or university and commonly consists of four years of study at an institution of higher learning. Like high school, the four undergraduate grades are commonly called freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior years (alternatively called first year, second year, etc.). Students traditionally apply for admission into colleges. Schools differ in their competitiveness and reputation; generally, the most prestigious schools are private, rather than public. Admissions criteria involve the rigor and grades earned in high school courses taken, the students' GPA, class ranking, and standardized test scores (Such as the SAT or the ACT tests). Most colleges also consider more subjective factors such as a commitment to extracurricular activities, a personal essay, and an interview. However, the Department of Education has forbidden any post-secondary educational institutions to deny a student because of extracurricular activities.
See Also[]
External Links[]
- Government webpage (Takes a while to load.)
- Official Government Website ((Fanon))

|
Allied States of America New Bay City FAC | |
| History & Economy | Struggle for Independence | Declaration of American Independence | Economy of the Allied States | |
| Government | Federal government | Executive | Legislature | Judiciary | Constitution | Laws (System) | Law enforcement | |
| Military | Department of Defense | Military | Army | Navy | |
| Politics | Confederate Party | Democratic Liberty Party | |
| People | Henry J. Fortis | Deven Carlson | John Romano | Trevor Prince | Timothy Mac | Beatrice Washton | Dana Erwin | James R. Eden | |